1.1 Data and Information
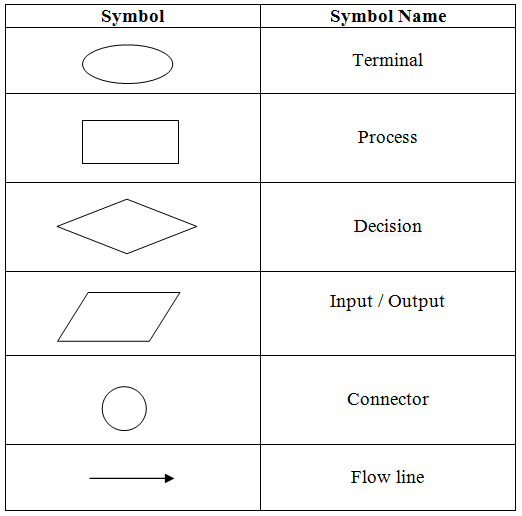
Figure 1.1 - Data Flow Diagram Symbols
📌 Example 1: Student Marks
Data: Ravi 78, 90, 79, 67, 76, 98
Information: When organized in a table with subject names, totals, averages, and ranks
| Name | Language | Maths | Science | Total | Average | Rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ravi | 78 | 90 | 79 | 468 | 78 | 2 |
📌 Example 2: NIC Number Analysis
NIC Number: 771234567V
- First 2 digits (77) = Year of birth (1977)
- Next 3 digits (123) = Day of the year
- If day number 0-4 = Male
- If day number 5-9 = Female
1.2 Information System
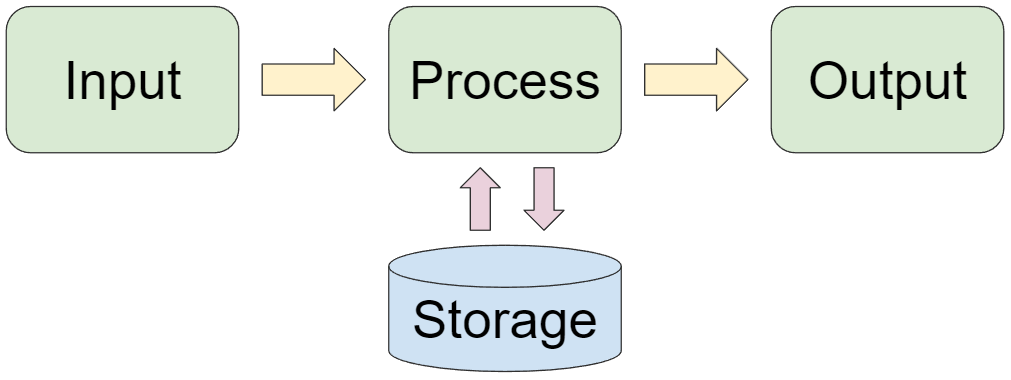
Figure 1.2 - Information System
Components of an Information System:
INPUT → PROCESSING → OUTPUT
↓
STORAGE
Examples of Information Systems:
🏦 1. ATM (Automatic Teller Machine)
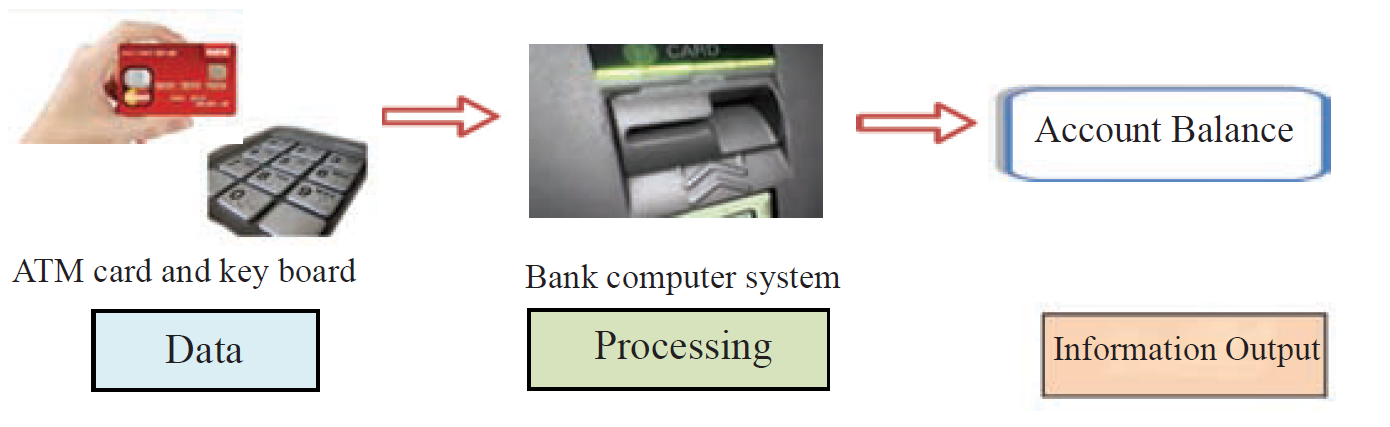
Figure 1.3 - ATM Machine
- Input: ATM card and PIN
- Processing: Bank computer system verifies
- Output: Account balance, cash withdrawal
👆 2. Fingerprint Reader
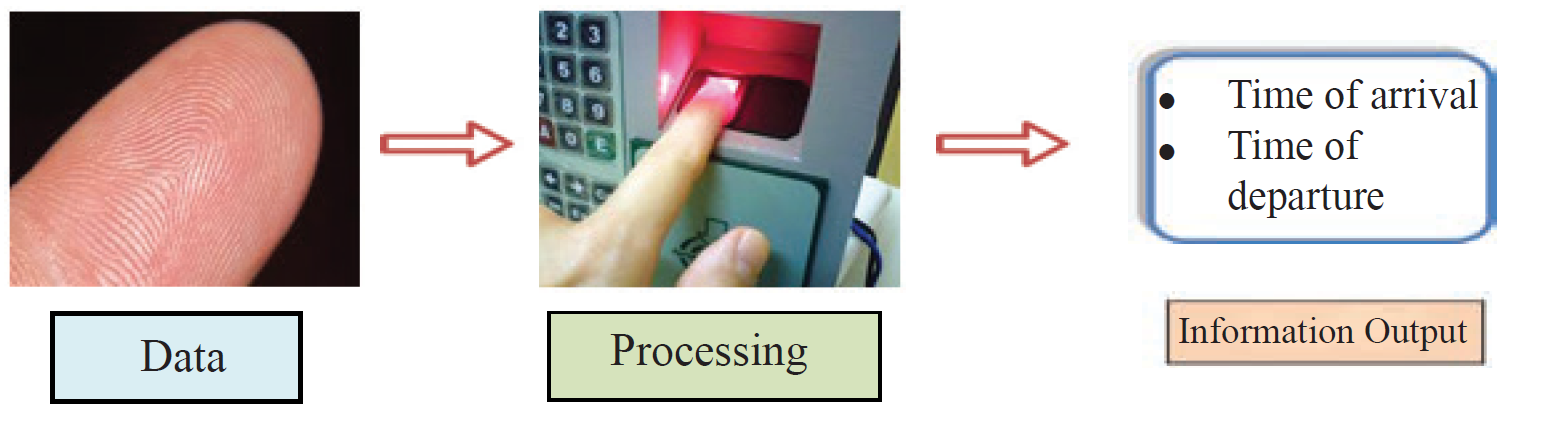
Figure 1.4 - Fingerprint Scanner
- Input: Fingerprint scan
- Processing: Matching with database
- Output: Time of arrival/departure
📱 3. QR Code Scanner
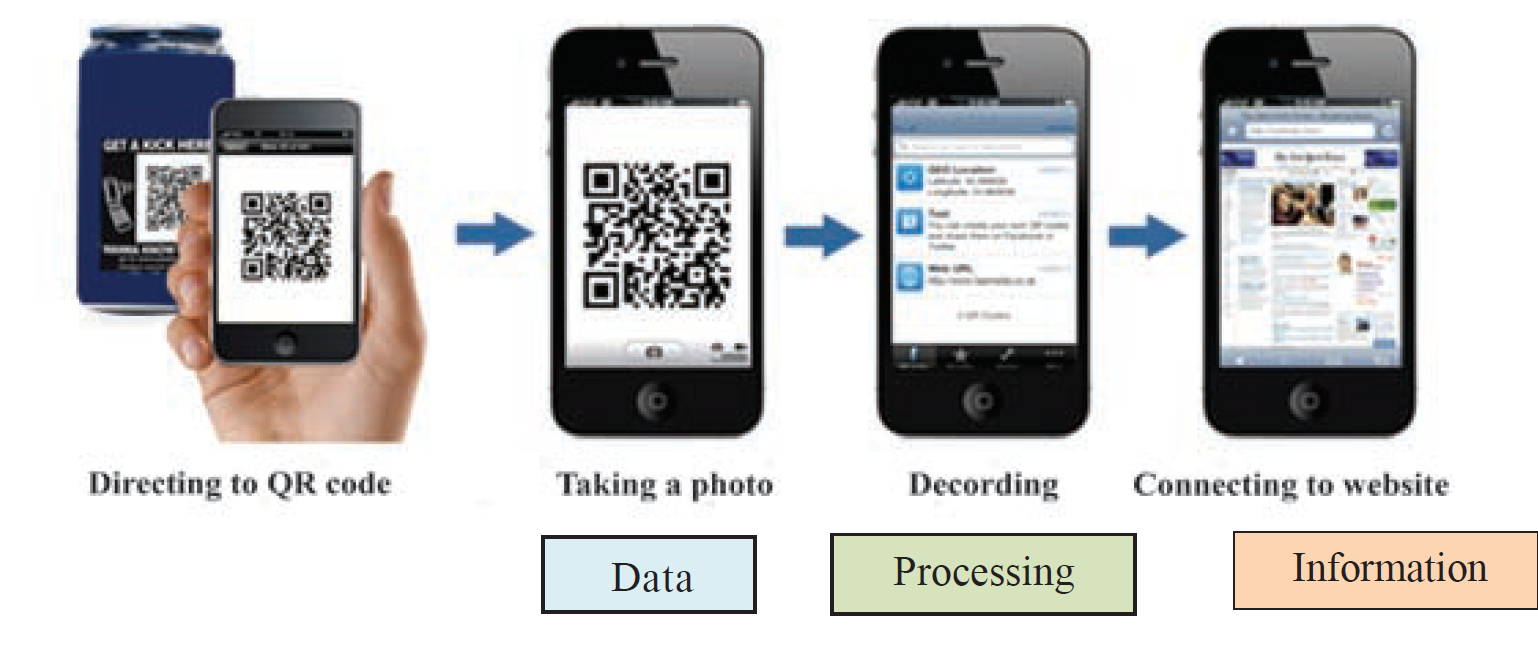
Figure 1.5 - QR Code Scanner
- Input: QR code image
- Processing: Decoding the pattern
- Output: Website link, product information
1.3 Characteristics of Quality Information
| Characteristic | Explanation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Relevancy | Information should be related to the requirement | Only highest qualification needed, not all grades from Grade 1 |
| Completeness | Information should be complete | Collecting data from entire population, not just small group |
| Accuracy | Information should be correct | Wrong patient information could harm treatment |
| Timeliness | Information should be up-to-date | Today's weather report for today's decisions |
| Cost Effectiveness | Cost of obtaining information should be reasonable | Don't spend more than the benefit gained |
1.4 Information and Communication Technology (ICT)
1.5 Applications of ICT
🏛️ 1. e-Government
- Easy access to government information
- Online services (birth certificates, vehicle registration)
- Saves time and reduces paperwork
- Transparent government processes
Examples: www.gov.lk, ICTA website, Government Information Center
📚 2. Education
Figure 1.7 - ICT in Education
a) In the Classroom
- Presentations and videos
- Educational games (Edutainment)
- CD-ROM learning materials
- Desktop publishing
b) Education - Anywhere, Anytime
Learning Websites:
- www.schoolnet.lk
- www.nenasala.lk
- www.e-thaksalawa.moe.gov.lk
c) Web-Based Training (WBT)
- Learn from home
- No travel costs
- Saves time
- Contact teachers via internet
d) Learning Management System (LMS)
| For Students | For School Management |
|---|---|
| Access learning materials anytime | Add quality learning materials |
| Upload assignments from home | Supervise activities and publish results |
| Submit queries through forums | Maintain student/teacher information |
| Participate in activities via video | Send emails to parents and officials |
e) Online Distance Learning
- Flexible time frame
- Digital library access
- Online assignments and quizzes
- Easy teacher consultations
🏥 3. Health Sector
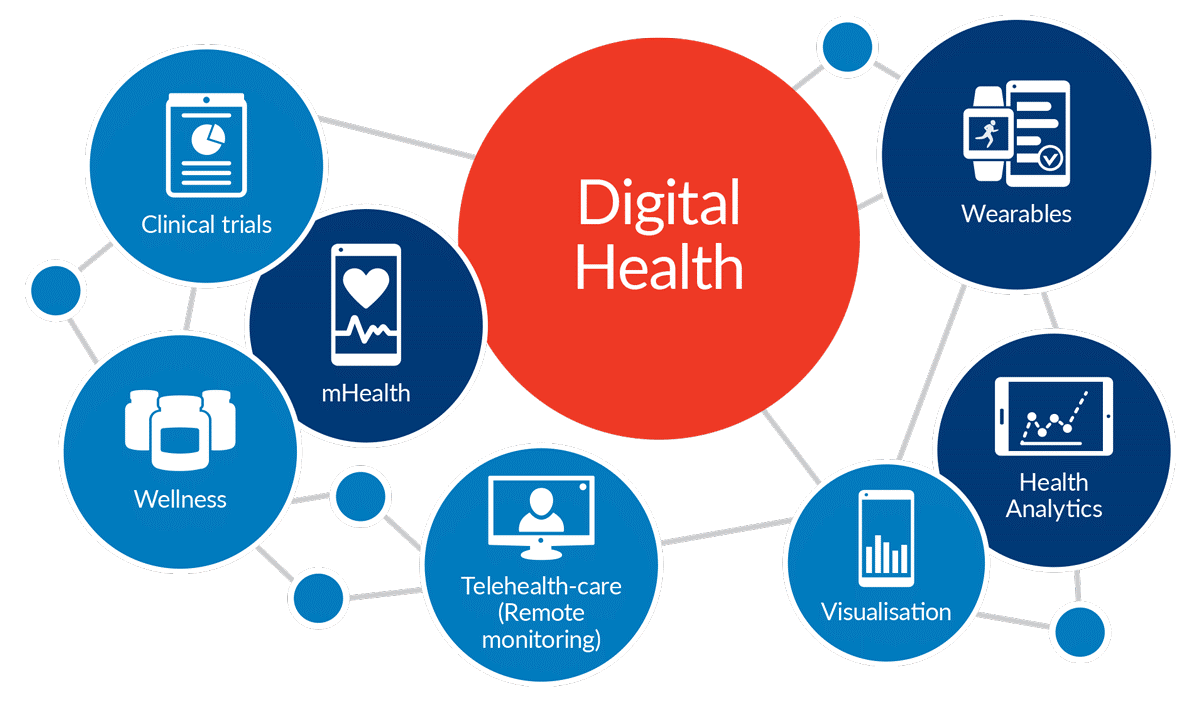
Figure 1.8 - Medical Technology
Medical Diagnosis Equipment:
🔬 CAT Scan (Computerized Axial Tomography)
CAT scan uses X-rays to quickly capture images. Creates 3D images of body parts for disease diagnosis
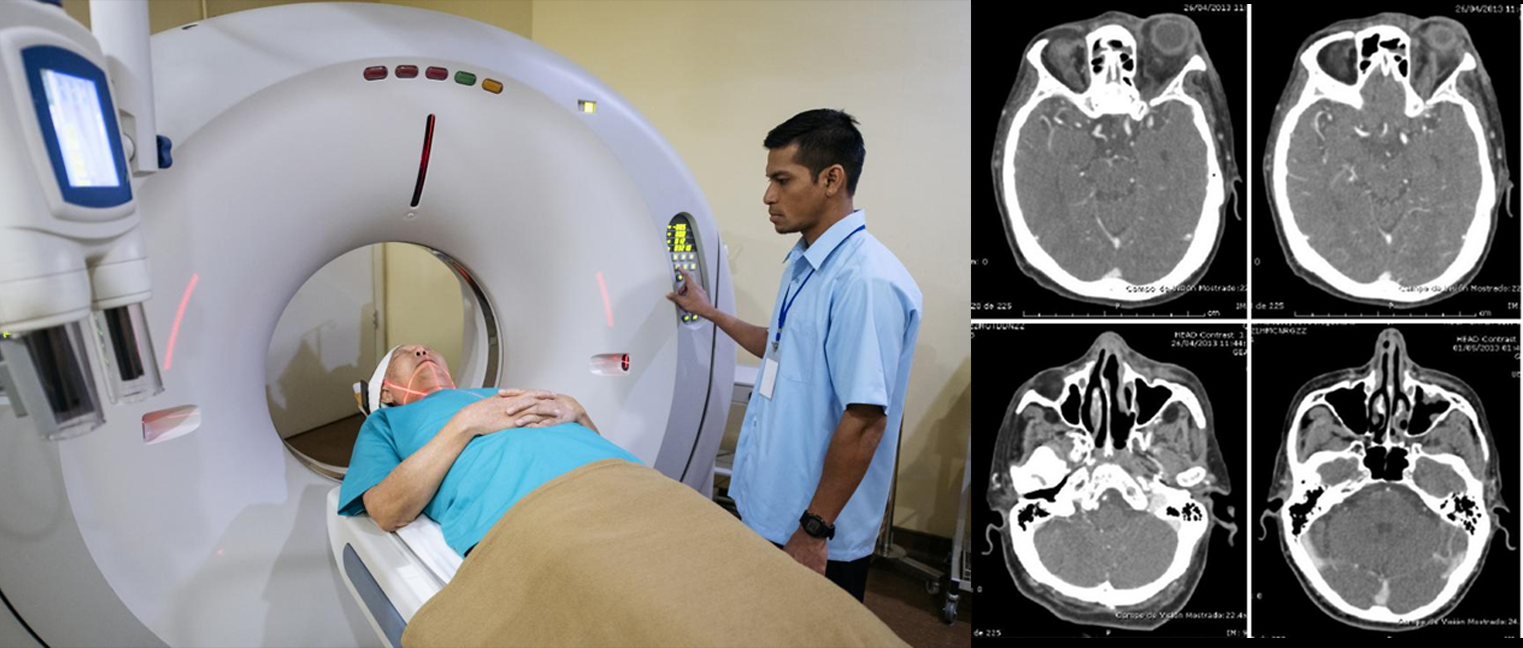
Figure 1.9 - CAT Scan
🧲 MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
Uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create digital images of internal organs. CT is faster and cheaper, but MRI offers superior soft tissue detail without radiation.
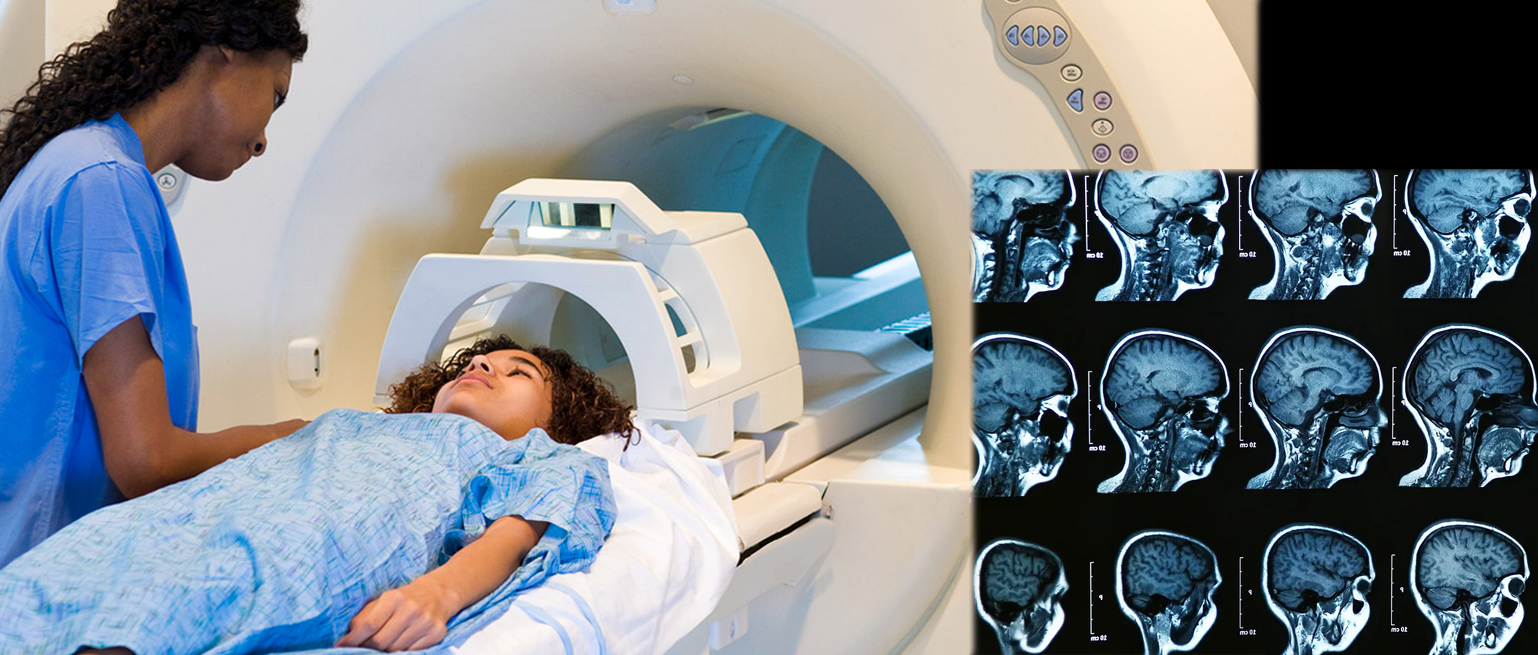
Figure 1.10 - MRI
💓 ECG (Electrocardiogram)
Monitors heartbeat by recording electrical impulses
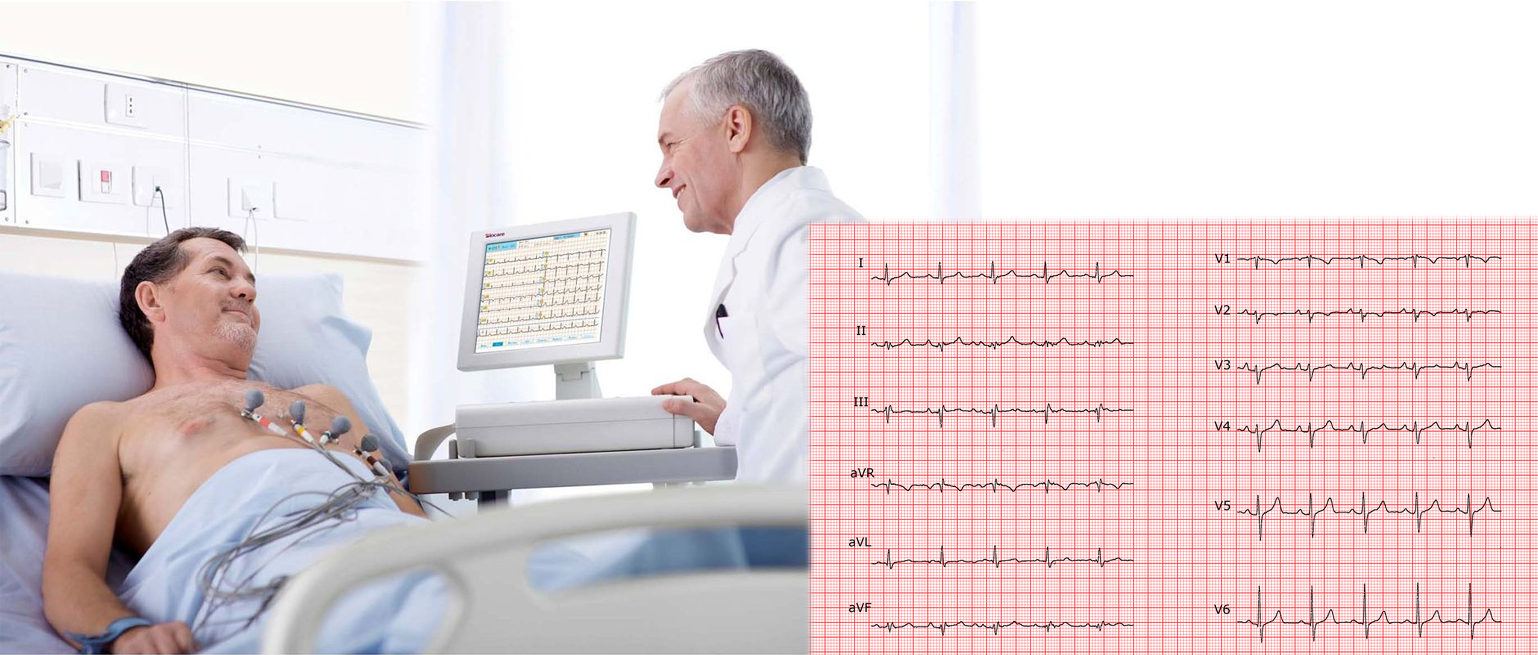
Figure 1.11 - ECG
🧠 EEG (Electroencephalography)
Records brain activities using electrical probes
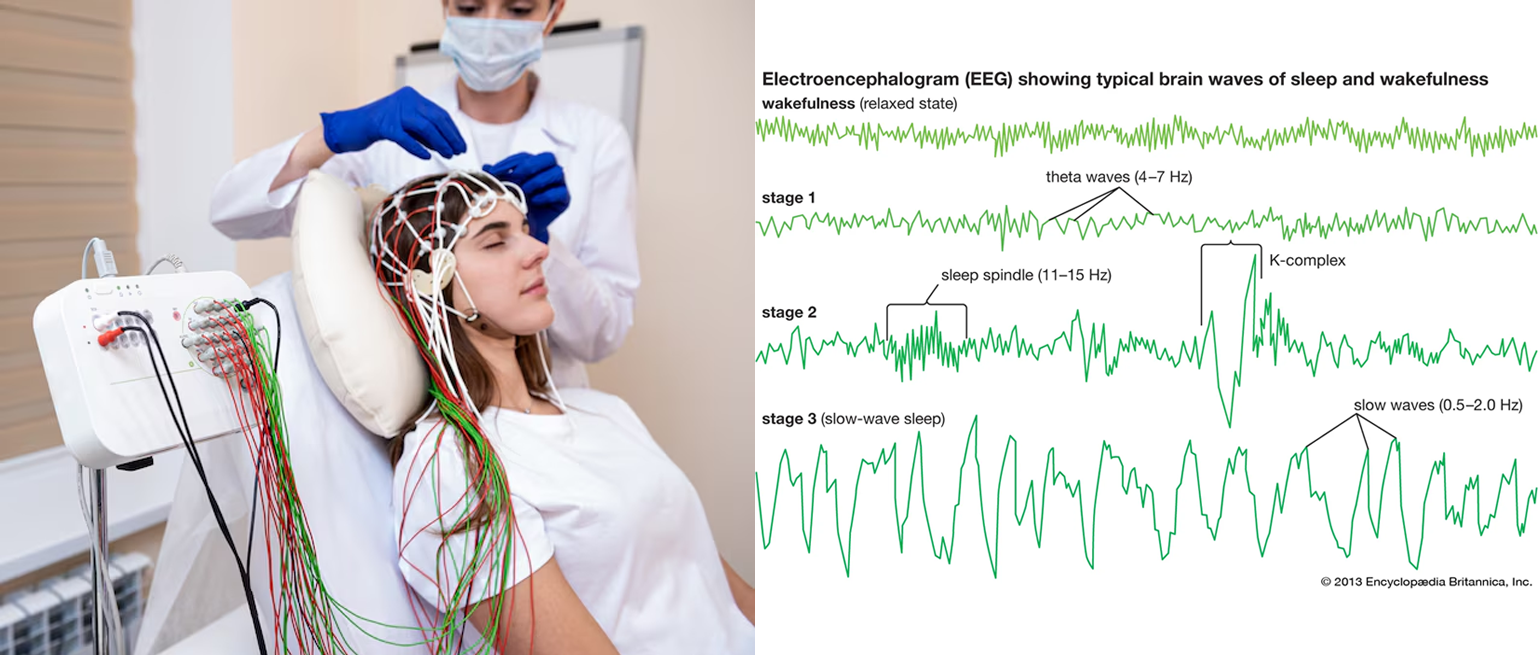
Figure 1.12 - EEG
Telemedicine:
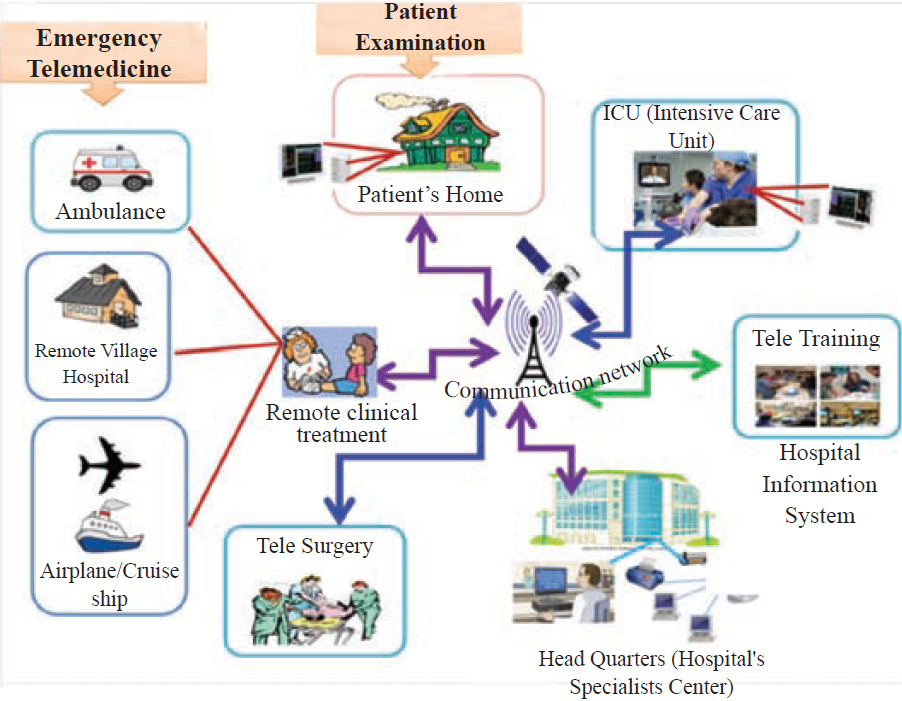
Figure 1.13 - Telemedicine
- Emergency Telemedicine: Emergency care via telecommunication
- Home Health Medicine: Monitoring patient at home via network
- Telemedicine Consultation: Seeking specialist advice remotely
- Telesurgery: Remote surgery with specialist consultation
- Medical Teletraining: Training hospital staff via telecommunication
🌾 4. Agriculture
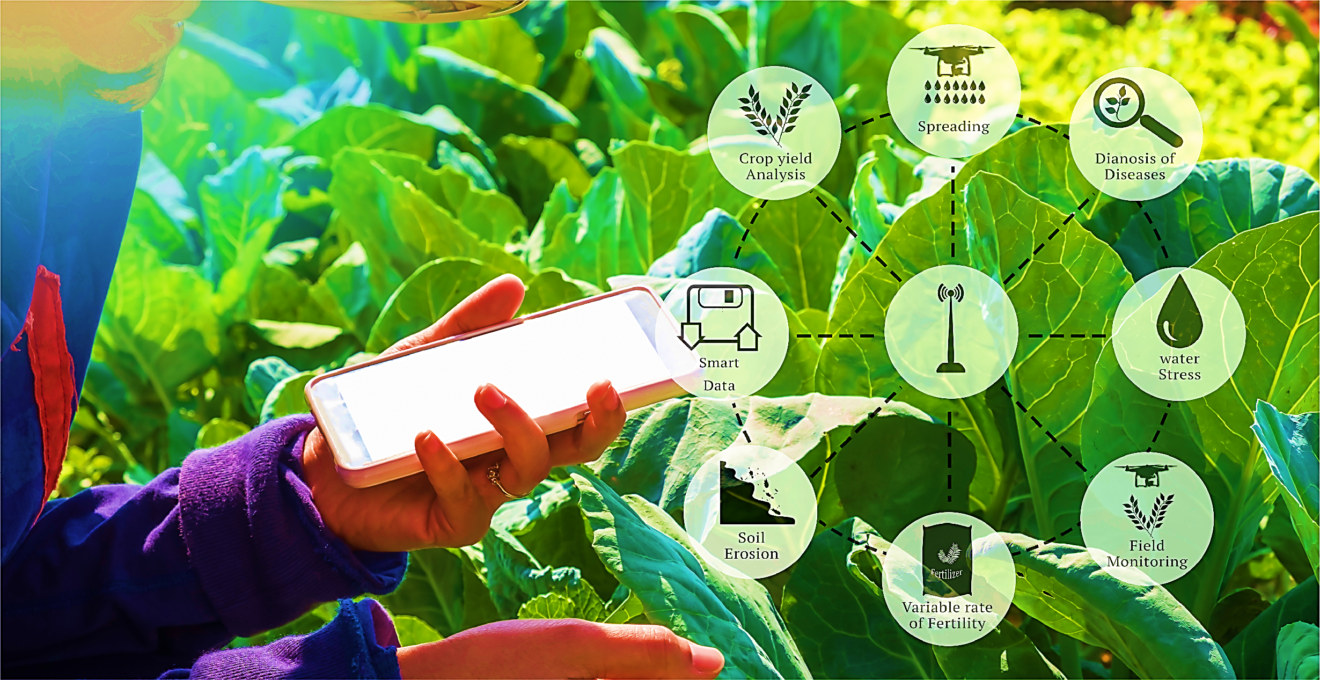

Figure 1.14 - ICT in Agriculture
Farming Devices:
- Meteorological Devices: Assess weather, rainfall, wind direction
- Automated Insect Control: Monitor insect population and movement
- Field Condition Sensors: Measure soil fertility and humidity
- Drip Irrigation: Automated water supply control
- Automatic Weed Remover: Identifies and removes weeds
- Robotic Planters: Plant seedlings in orderly manner
- Harvesting Robots: Monitor growth and harvest crops
- Greenhouse Technology: Control light, moisture, and air
Farm Management:
- RFID: Identify, count, and locate animals
- Automated Milking: Monitor cow health and milk quality
- CCTV: Security from animals and thieves
- Farm Management Software: Track profits, losses, salaries
Fishing Industry:
Sensors in the sea convey information about fish concentration to fishing trawlers via internet.
🏭 5. Manufacturing and Business
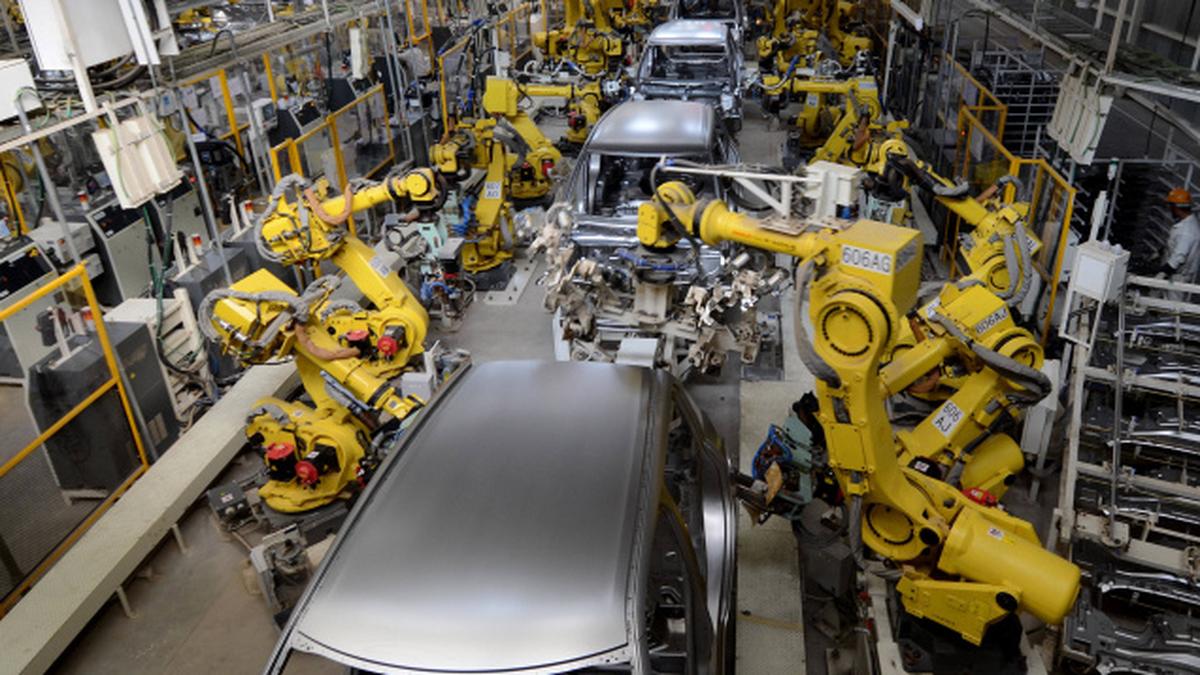

Figure 1.15 - Robots in Manufacturing
Benefits of Robots in Manufacturing:
- 24-hour service
- Never get tired
- High efficiency
- Accuracy
- Hygiene
- Reduces cost of production
- High-quality products
Business Applications:
💼 Video Conferencing
Face-to-face meetings while at different locations
Benefits: Saves time, travel cost, and effort👤 Human Resource Management
- Fingerprint scanner for attendance
- Card reader for identity management
- Automatic salary calculation
- Leave record management
🏦 e-Banking System

- ATM cash withdrawal anytime, anywhere
- Inter-banking transactions via internet
- Pay utility bills through mobile
- Check account balance remotely
🛒 Online Shopping (e-Commerce)

- Shop from global companies
- Open 24 hours
- Shop from convenient place
- Electronic payment (credit cards)
- Home delivery
- Saves time and transport cost
🚗 6. Transport
- CCTV: Monitor traffic, accidents, illegal activities
- Traffic Light Control: Automated lights at junctions
- Parking Identification Placard: Automated gate opening for registered vehicles
🎮 7. Entertainment
- Social networking
- Listening to music and watching videos
- Watching missed TV programs online
- Digital photography
- Video games
- e-Books and e-News
- High-definition video streaming
1.6 Demerits of ICT
- Addiction: Excessive computer/internet use affecting education
- Health Issues: Sore eyes, back pain, headache, obesity
- Unsuitable Friendships: Building wrong connections via social media
- Computer Viruses: System damage due to improper internet use
- Mental Disorders: Visiting improper websites
- Privacy Violation: Publishing distorted photos/videos
- Social Isolation: Less physical interaction
- Copyright Violation: Illegal use of content
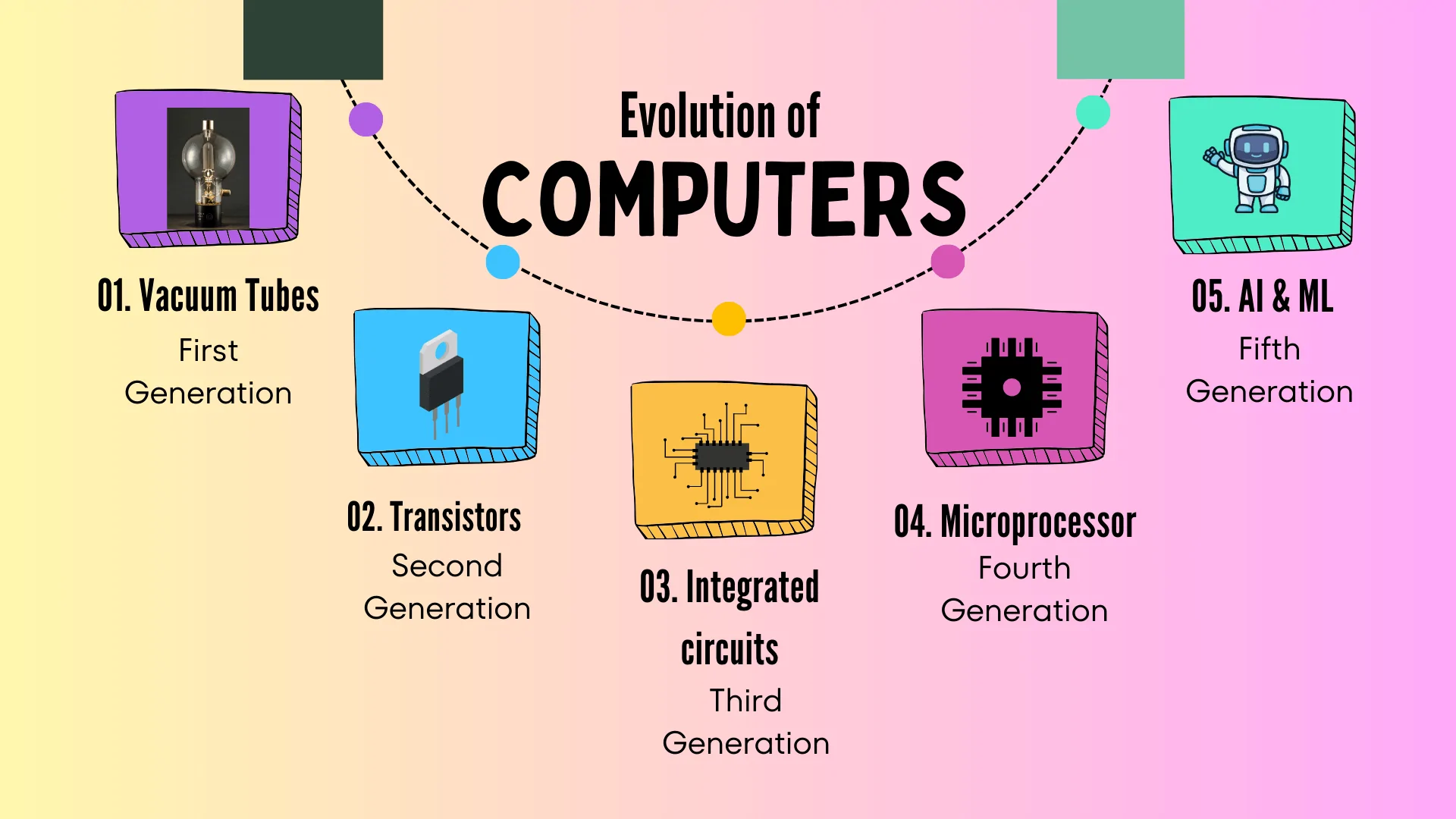
1.7 Evolution of the Computer
Important Inventors:
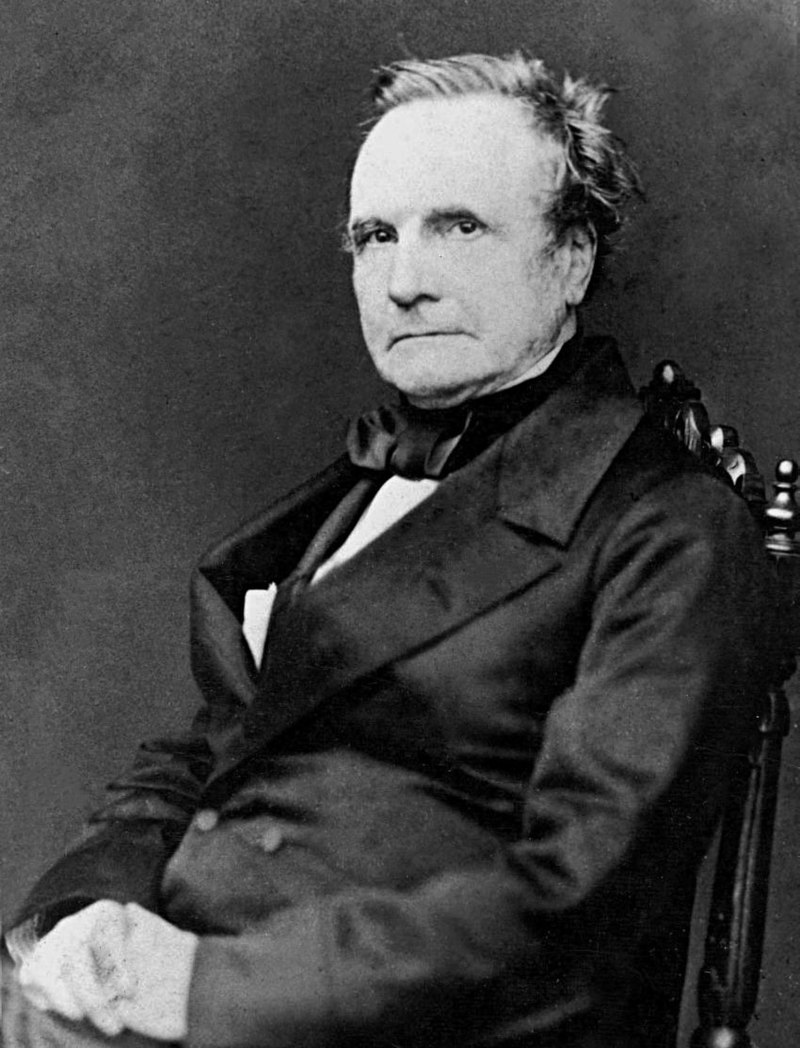

Charles Babbage - Father of Computing
- 1642 - Blaise Pascal: Invented Adding Machine (first mathematical machine)
- 1674 - Gottfried Wilhelm Von Leibnitz: Improved Pascal's machine to perform multiplication and division
- Joseph Jacquard: Invented mechanical loom using Punch Card System
- Charles Babbage: Started Analytical Engine using Punch Card concept - Called "Father of Computing"
- Ada Augusta Lovelace: First programmer (wrote programs for Analytical Engine)
- 1944 - Howard Aiken: Invented MARK 1 (Automatic Sequence Control Calculator)

Ada Lovelace - First Computer Programmer
Computer Generations:
🖥️ First Generation (1940-1956)
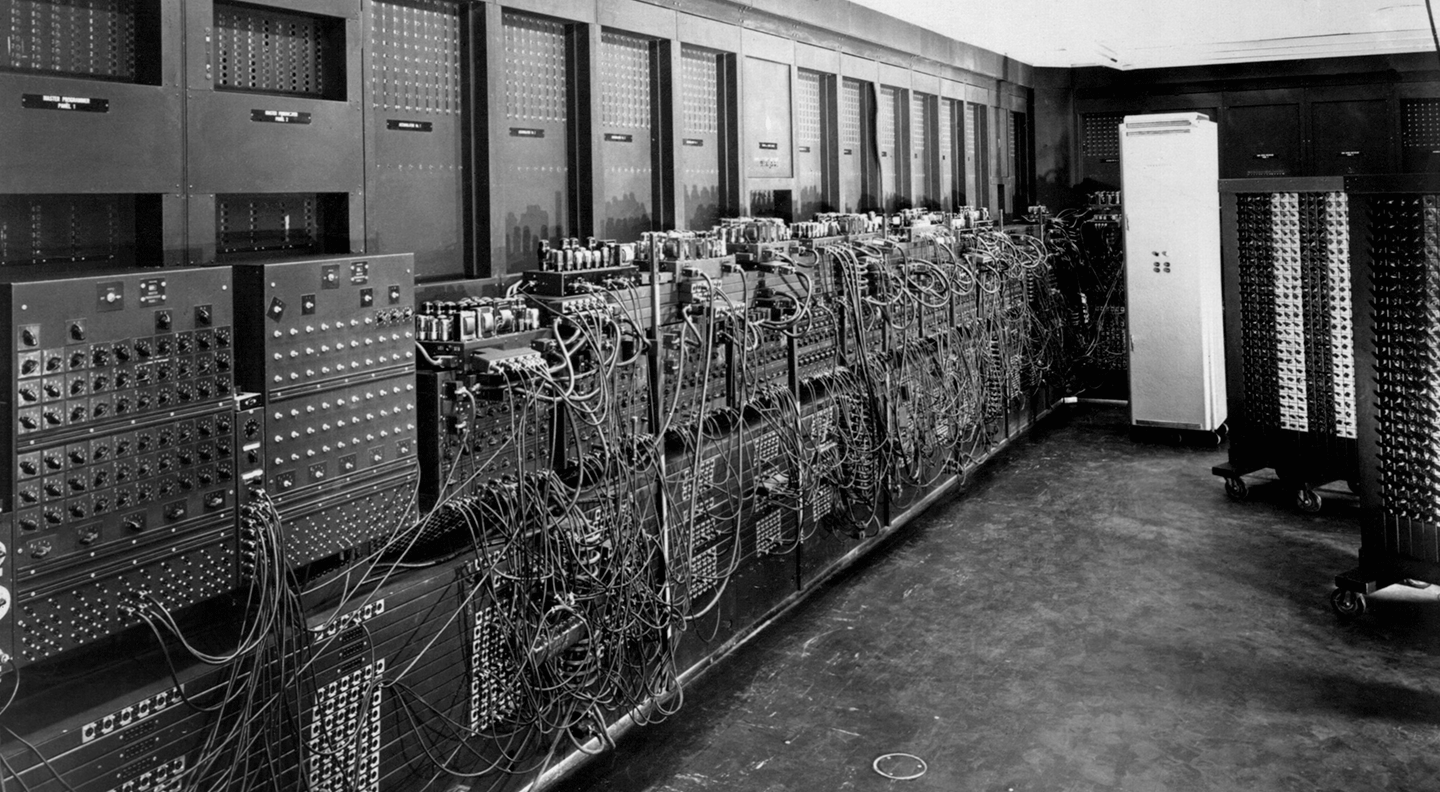
ENIAC - Electronic-Numerical-Integrator-And-Computer - First Generation Computer
Technology: Vacuum Tubes, Punch Cards
Examples: ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC, IBM 701
Characteristics:
- Large in size
- High heat generation
- Slow processing
- High power consumption
- Very expensive
Software: Machine language, Assembly language
🖥️ Second Generation (1956-1963)
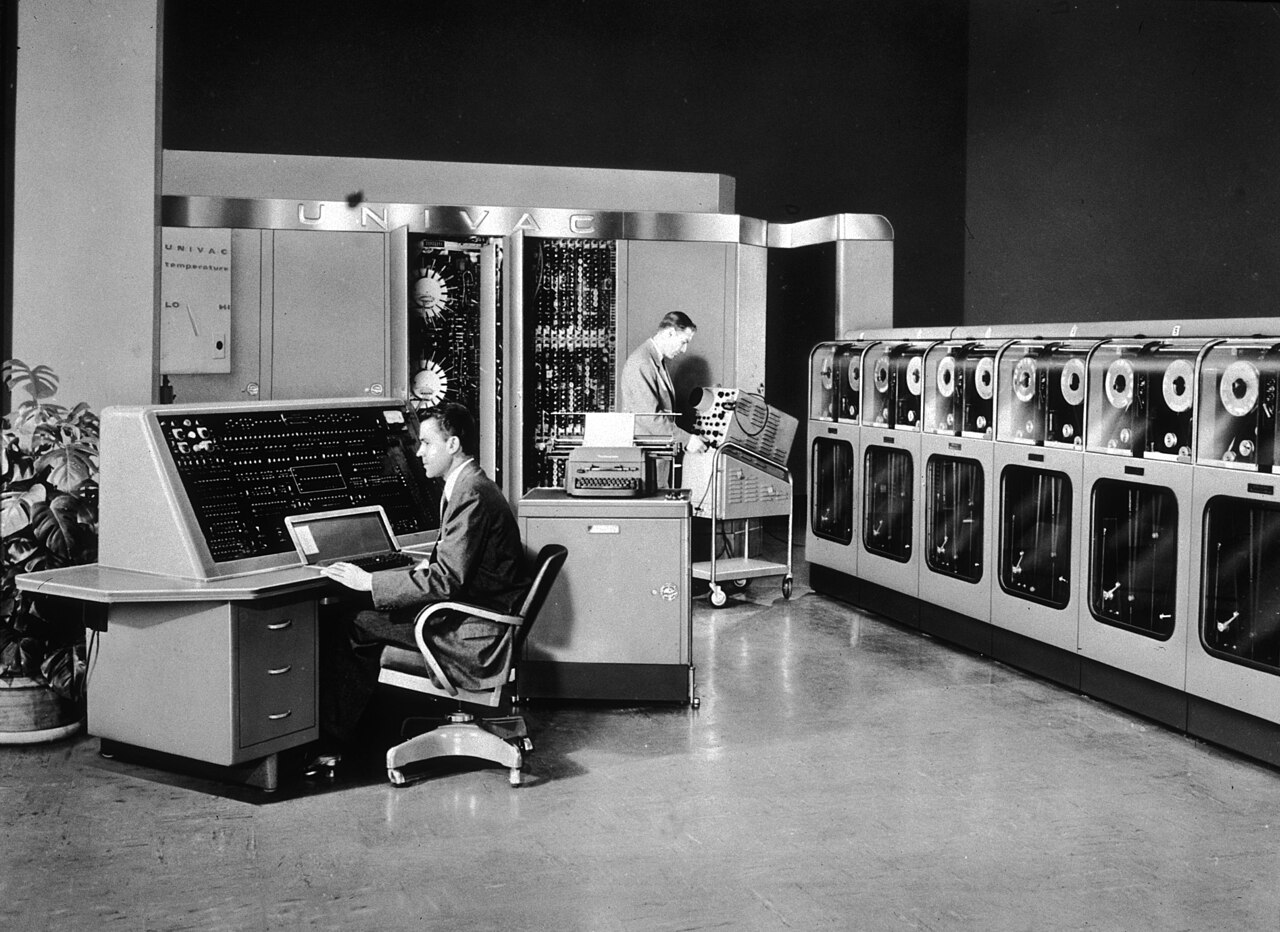

UNIVAC - Universal Automatic Computer - Transistors replaced Vacuum Tubes
Technology: Transistors, Magnetic Tapes, Floppy Disks
Examples: IBM 7030, CDC 1604, UNIVAC LARC
Characteristics:
- Smaller in size
- Less heat generation
- Faster than first generation
- Lower power consumption
- Still expensive
Software: High-level programming languages
🖥️ Third Generation (1964-1975)
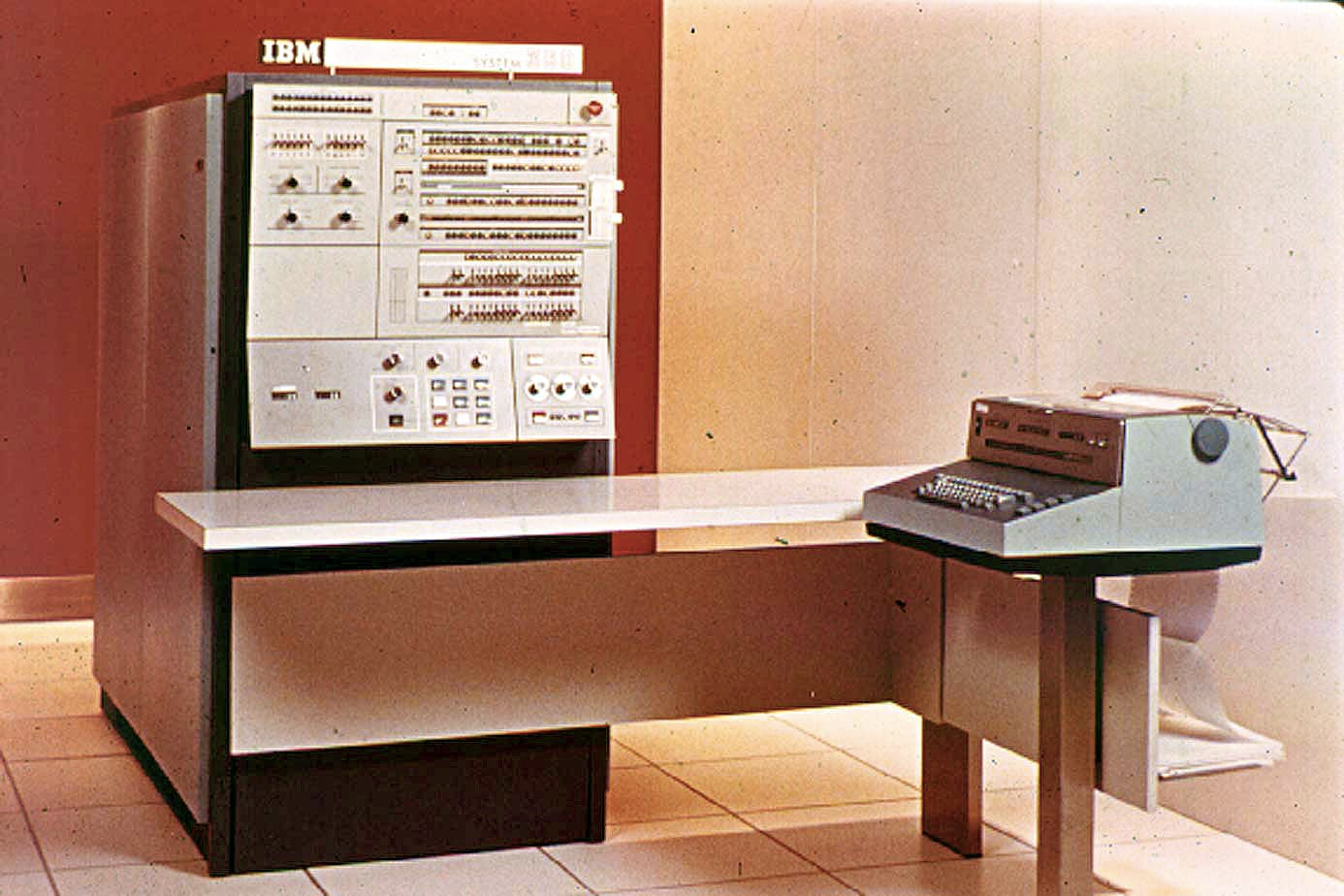
PDP-8 - Third Generation Computer
Technology: Integrated Circuits (IC), High-capacity disks
Examples: IBM-360/370, PDP-8, PDP-11
Characteristics:
- Much smaller in size
- Less heat generation
- Faster processing
- Low power consumption
- More affordable
Software: Operating Systems (OS), Well-developed programming languages
🖥️ Fourth Generation (1975-1989)
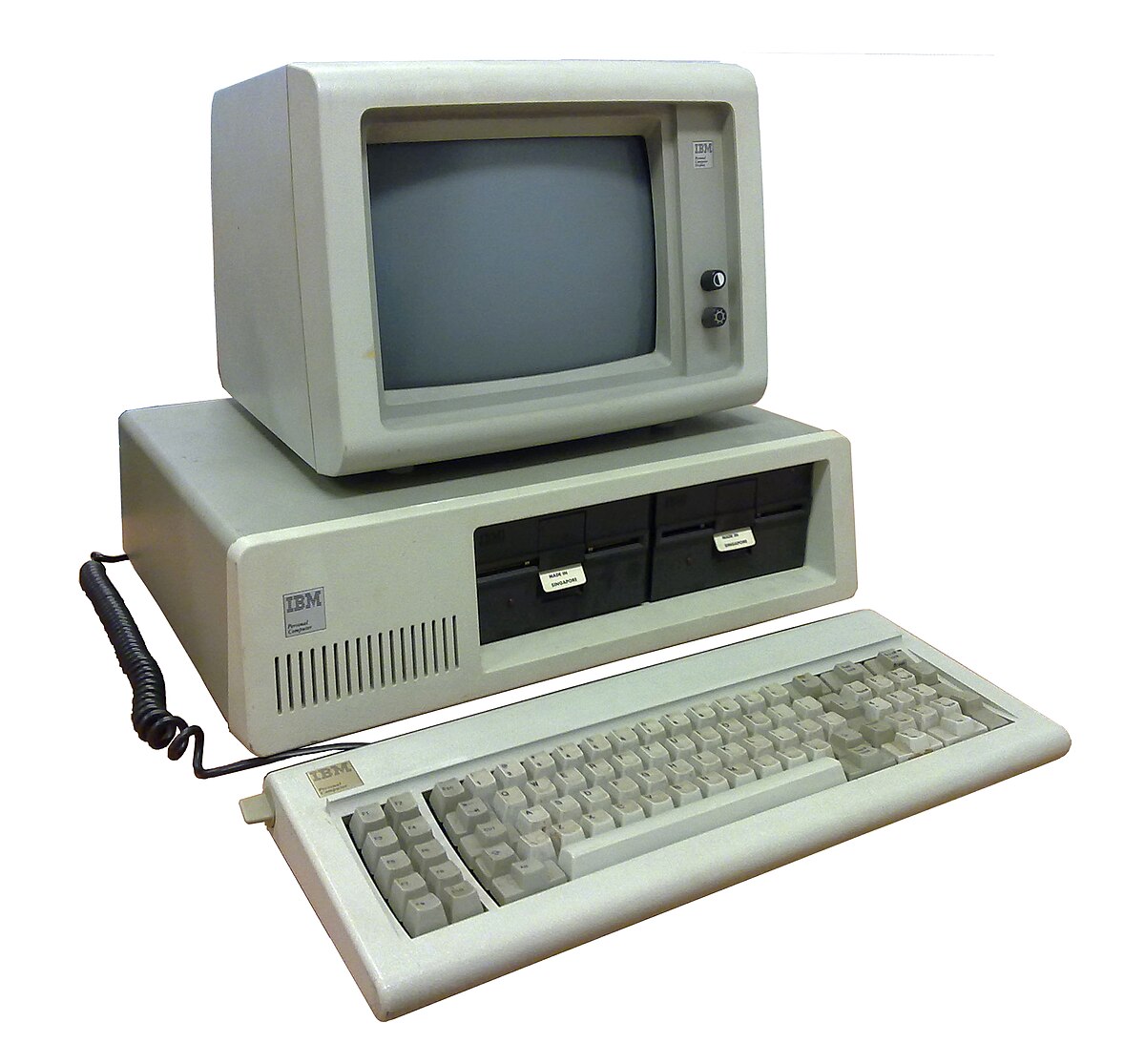

IBM PC - Fourth Generation Personal Computer
Technology: Microprocessors, VLSI (Very Large Scale Integration)
Examples: IBM PC, Apple II
Characteristics:
- Very small and portable
- Personal computers (PC) introduced
- Upgradable
- Affordable
- High-capacity storage
Software: GUI Operating Systems, UNIX OS
🖥️ Fifth Generation (1989-Present)
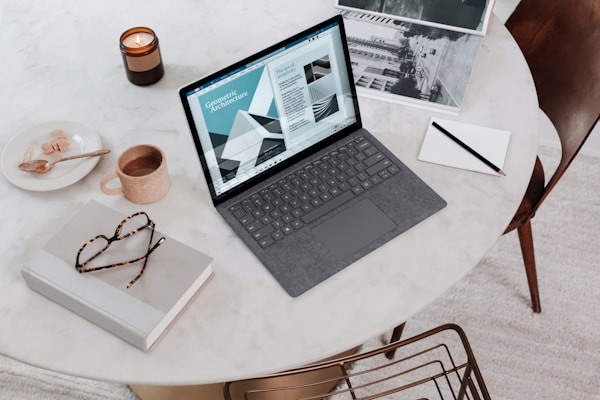

Modern Laptops and Portable Computers
Technology: ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration), Internet
Examples: IBM notebooks, Pentium PCs, Workstations
Characteristics:
- Highly portable
- Very powerful and efficient
- Less expensive
- Easy to operate
- High reliability
Software: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Voice recognition, Internet and multimedia applications
📝 Practice Questions & Answers
Q1. Define data and information with examples.
Data: Numbers, words, images, and symbols that do not have meaning when standing alone.
Example: 78, 90, 79, 67 (just numbers)
Information: Meaningful data obtained by processing and organizing data.
Example: Student marks organized in a table showing Name, Subject, Total, Average, and Rank.
Q2. What are the characteristics of quality information?
1. Relevancy: Information should be related to the requirement
2. Completeness: Information should be complete
3. Accuracy: Information should be correct and error-free
4. Timeliness: Information should be up-to-date
5. Cost Effectiveness: Cost of obtaining information should be reasonable
Q3. What is an Information System? Explain with components.
An Information System is a combination of components that work together to fulfill a task of processing data into information.
Components:
• INPUT: Submitting data for processing
• PROCESSING: Converting data into information
• OUTPUT: Presenting the processed information
• STORAGE: Storing data and information for future use
Q4. Give three examples of Information Systems in daily life.
1. ATM Machine: Input: ATM card and PIN → Processing: Bank verification → Output: Cash and account balance
2. Fingerprint Reader: Input: Fingerprint → Processing: Pattern matching → Output: Attendance time record
3. QR Code Scanner: Input: QR code → Processing: Decoding → Output: Product information/website link
Q5. What is e-Government? List three benefits.
e-Government: When a government communicates with its citizens, companies, organizations, and other governments using ICT.
Benefits:
1. Easy access to government information and services
2. Online services reduce paperwork and save time
3. Transparent government processes
4. Citizens can access services from home
Q6. Explain how ICT is used in education.
In the Classroom: Presentations, educational videos, interactive games, CD-ROM learning
Anywhere, Anytime Learning: Educational websites (e-thaksalawa, nenasala), Web-Based Training (WBT)
Learning Management System (LMS): Upload assignments, access learning materials, participate in forums
Distance Learning: Connect with universities worldwide for higher education
Teaching Aid: Teachers use presentations, animations, and online resources
Q7. What is Telemedicine? Give three examples.
Telemedicine: Using ICT to examine and provide healthcare to patients who are far from the hospital.
Examples:
1. Emergency Telemedicine: Providing emergency care to remote patients via telecommunication
2. Home Health Medicine: Monitoring patient's health at home using networked systems
3. Telesurgery: Performing surgery with specialist consultation from a distant location
Q8. List five medical diagnosis machines that use ICT.
1. CAT Scan: Creates 3D images of body parts
2. MRI: Creates digital images using magnetic fields
3. ECG: Monitors heartbeat and electrical impulses
4. EEG: Records brain activities
5. Blood Sugar Testing Machine: Analyzes blood glucose levels
Q9. How does ICT help in agriculture?
Farming:
• Meteorological devices assess weather and rainfall
• Automated insect control devices monitor pests
• Drip irrigation controls water supply
• Robotic planters and harvesters
• Greenhouse technology controls environment
Farm Management:
• RFID tracks and counts animals
• Automated milking machines
• CCTV for security
• Computer software for profit/loss calculations
Q10. What are the benefits of robots in manufacturing?
1. Work 24 hours without rest
2. Never get tired
3. High efficiency and accuracy
4. Maintain hygiene standards
5. Reduce production costs
6. Produce high-quality products
7. Minimize human errors
Q11. Explain e-Banking and its advantages.
e-Banking: Banking services provided through electronic means (internet, mobile phones).
Advantages:
1. Withdraw cash anytime at ATM machines
2. Inter-banking transactions via internet
3. Pay utility bills through mobile phones
4. Check account balance remotely
5. No need to visit bank physically
6. Saves time and travel costs
Q12. What are the demerits of ICT?
1. Addiction: Excessive use affecting education and daily life
2. Health Issues: Eye strain, back pain, headache, obesity
3. Unsuitable Friendships: Wrong connections via social media
4. Computer Viruses: System damage from improper internet use
5. Mental Disorders: Visiting inappropriate websites
6. Privacy Violation: Publishing distorted photos/videos
7. Social Isolation: Less physical human interaction
8. Copyright Violation: Illegal use of content
Q13. Name the "Father of Computing" and explain why.
Charles Babbage is called the "Father of Computing."
Reason: He designed the Analytical Engine using the Punch Card System concept. This machine was based on the concepts of input, process, output, and storage - the fundamental concepts that helped in the development of modern computers.
Q14. Compare First Generation and Fifth Generation computers.
| First Generation (1940-1956) | Fifth Generation (1989-Present) |
|---|---|
| Used Vacuum Tubes | Uses ULSI technology |
| Very large in size | Highly portable |
| High heat generation | Very less heat generation |
| Slow processing | Very fast processing |
| Very expensive | Less expensive |
| Machine language | AI, multimedia, GUI |
Q15. What is Online Distance Learning? List its features.
Online Distance Learning: Connecting with universities or learning centers via internet to pursue higher education from any location.
Features:
1. Flexible time frame for learning
2. Digital library facility
3. Online assignments and quizzes
4. Contact with teachers online
5. Easy teacher consultations
6. Learn from home or any convenient place
7. Lower cost compared to traditional education
Q16. Explain the difference between data and information using the NIC number example.
Data: The NIC number "771234567V" appears as just a number
Information: When analyzed:
• First 2 digits (77) = Year of birth (1977)
• Next 3 digits (123) = Day number of the year
• Digit 0-4 indicates male
• Digit 5-9 indicates female
Therefore, we can determine the person's date of birth and gender from the NIC number.
Q17. What is a Learning Management System (LMS)? How does it benefit students?
LMS: A system used to manage school and higher education activities via internet.
Benefits for Students:
1. Access learning materials anytime, anywhere
2. Upload assignments from home
3. Submit queries and get replies through forums
4. Participate in co-curricular activities via video
5. Parents can monitor progress from home
Q18. List five robotic applications in agriculture.
1. Seedling Planters: Plant seedlings in orderly manner across large fields
2. Automatic Weed Removers: Identify and remove weeds while preserving crops
3. Crop Harvesting Robots: Monitor plant growth and harvest in large farmlands
4. Automated Milking Machines: Monitor cow health and milk quality
5. Drip Irrigation Systems: Control water supply based on programmed data
Q19. What are the advantages of Online Shopping (e-Commerce)?
1. Select from any global company on the internet
2. Open 24 hours a day
3. Shop from any convenient place
4. Electronic payment methods (credit cards)
5. Home delivery of products
6. Saves time and transport costs
7. Avoid travel-related exhaustion
8. Easy comparison of products and prices
Q20. Write short notes on: (a) Video Conferencing (b) RFID (c) Greenhouse Technology
(a) Video Conferencing:
Technology enabling face-to-face meetings between people at different locations. Saves time, effort, and travel costs. No need for special venue.
(b) RFID (Radio Frequency Identification):
Device used in farm management to identify, count, and locate animals in large areas. Uses radio frequency signals.
(c) Greenhouse Technology:
Protected environment for crops using ICT to control light, moisture, and air. Protects from natural disasters and pests. Produces high-quality rare crops.
📌 Key Points to Remember
- Data → meaningless when alone; Information → meaningful after processing
- Information System: INPUT → PROCESSING → OUTPUT + STORAGE
- Quality Information: Relevant, Complete, Accurate, Timely, Cost-effective
- ICT = Information + Communication Technology
- Major ICT Applications: e-Government, Education, Health, Agriculture, Business, Transport, Entertainment
- Use ICT responsibly to avoid addiction, health issues, and privacy violations
- Computer evolution: Abacus → Mechanical → 5 Generations (Vacuum Tubes → Transistors → IC → Microprocessors → ULSI)
- Charles Babbage = Father of Computing; Ada Lovelace = First Programmer